What
Redesigned IKEA's Sustanability features. Improved navigation of the website and integrated their goals that align with IKEA's mission.
How
Conducted a Heauristic Evaluation of the website and usability tested the sustanbility services. From the data, I redesigned the user flow for those features.
Leadership
A few months after this case study, IKEA indeed redesigned their website. While the website ultimately took a different form, it reflects the core recommendations I provided, demonstrating my ability to detect problems and design solutions that anticipate real-world outcomes.
Objective
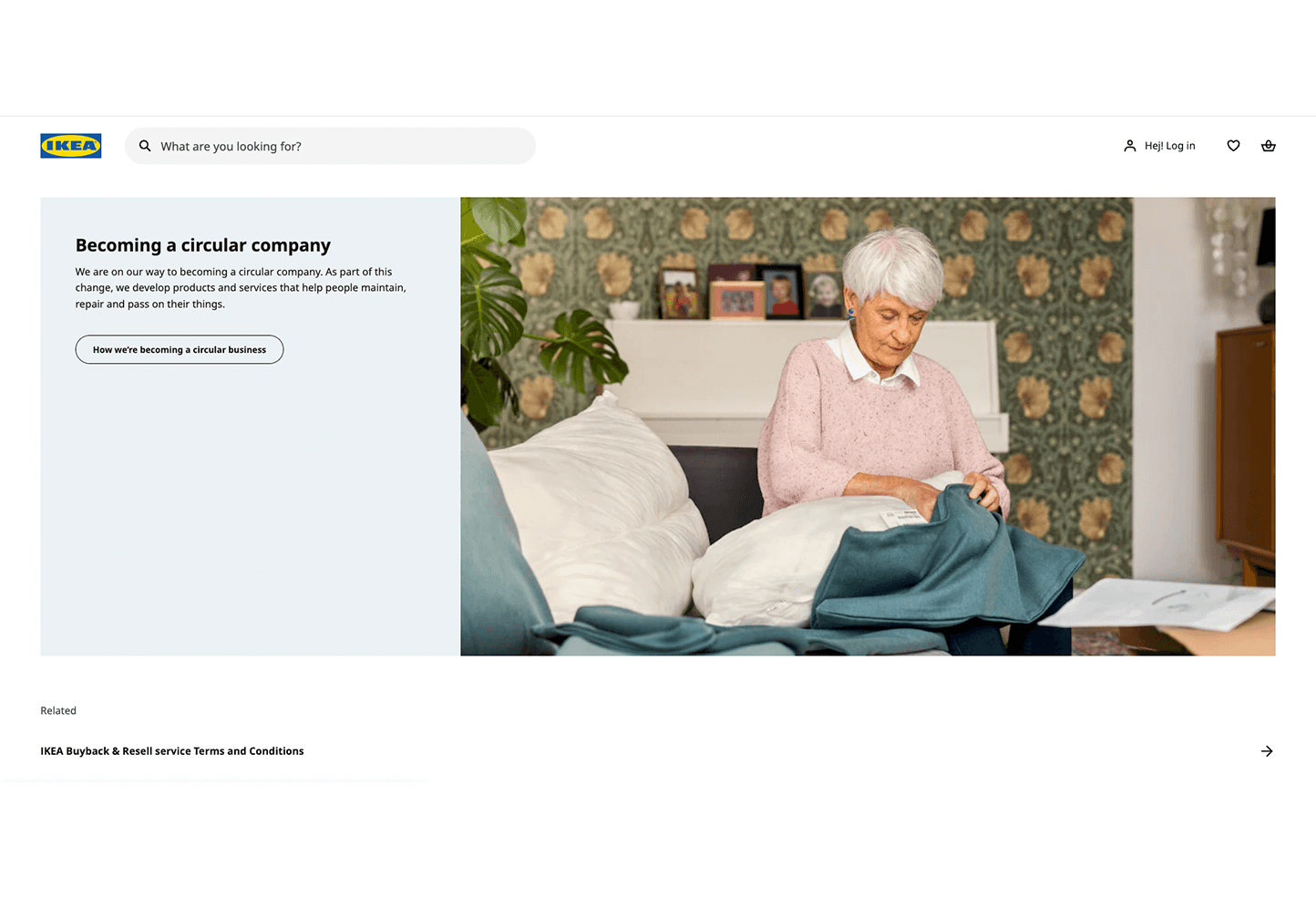
IKEA’s 2021 financial report highlighted a strong focus on sustainability, with goals to become climate-positive by 2030 and active involvement in COP26. The IKEA Place app leverages augmented reality but has usability issues beyond the scope of this study.
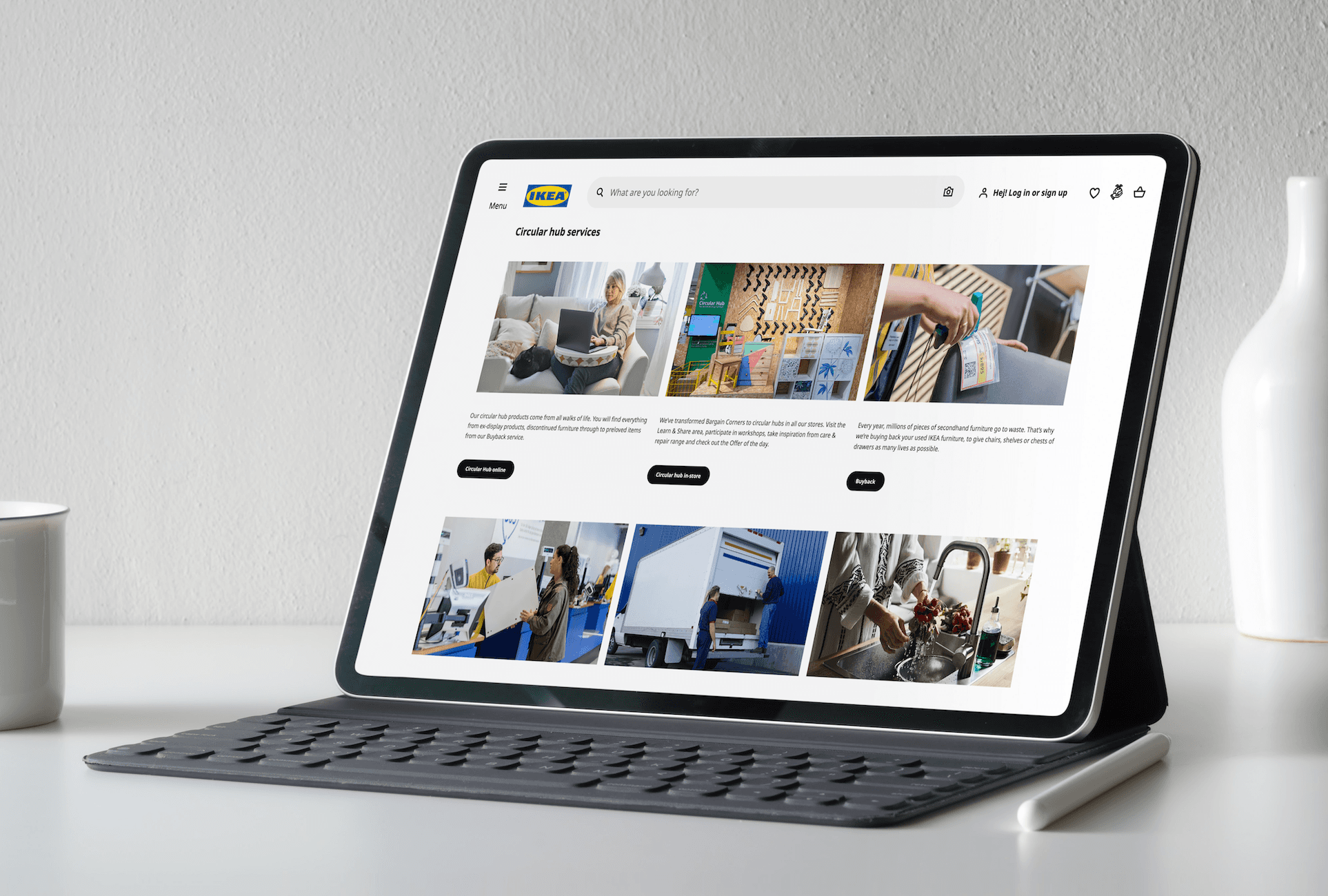
The previous website layout was simple but has issues like inconsistent fonts, poorly categorised menus, and a lack of engaging visual appeal. Key information may be missed unless users scroll to the footer.
This study aimed to evaluate how easily users could find sustainability-related information and services and whether the experience was user-friendly and engaging.
Heuristic Evaluation
For my evaluation I set a few usability standards to insure IKEA's design reflected its goals. Here is the rationale behind the design standards:
Consistency and Standards
Interfaces should avoid including unnecessary or irrelevant information.Recognition Rather than Recall
Shortcuts, which may be hidden from beginners, can help experienced users interact more efficiently. This approach allows the design to serve both novice and expert users.Flexibility and Efficiency of Use
Reduce the user’s memory burden by making elements, actions, and options visible. Details needed for using the service should be visible or easy to access when necessary.Aesthetic and Essential Design
Users shouldn’t need to guess if different terms, contexts, or actions mean the same thing. Jakob’s Law states that users' expectations are shaped by their experiences with other digital products they use frequently. If consistency is not maintained, users may face increased cognitive strain as they are forced to learn something new.
Usability Study
In this usability test, the CIF method proves effective as sustainability features are not central to this organisation. By measuring time on task and user experience when selecting these services, significant website issues can be identified and addressed. Given that this is an “auxiliary” service, even minor difficulties may lead users to abandon the task or avoid seeking more sustainable options, potentially underutilising the organisation’s offerings.
An A/B test compared user experiences on desktop and mobile versions of the website. Half of the participants completed tasks on personal computers, and the other half on mobile devices. Since many users browse furniture and décor casually before making a purchase decision or visiting a store, this multi-channel data comparison enhances the study’s relevance to real-world behaviour.
Card Sorting
Since a key issue faced by users was not knowing the services that IKEA provides under sustanibility initiatives or what they might be called, it was important to perform a card sorting exercise. This helped to improve site map and hierarchal tasks of the website.
Accessibility Evaluation
The persona “Simone” was randomly selected from the UK Gov Personas. She is a dyslexic user.
It is recommended for dyslexic users, websites must avoid using justified text and italics. And the website does not use them.
A browser extension called “dyslexia friendly” was installed to simulate Simone’s condition. This is how the webpage looks when it is enabled.
The Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool (WAVE) was used to generate the following statistics on the Ikea website.
Another requirement for dyslexic users is to have well-structured hierarchy in the web applications they use . From the Wave evaluation tool 8 navigation errors were found. There were no contrast issues found on this website.
Design recommendations and Re-design
The researcher makes the following redesign recommendations:
Title heading unclear: Use clearer, more descriptive titles for the feature, avoiding niche terminology. Priority: Must.
Service awareness: Place a brief description of these services on the homepage to improve visibility. Priority: Must.
Sustainability features: Create a dedicated section on the homepage or menu to highlight sustainability offerings. Priority: Must.
Van hire cost calculation: Add a cost calculator to the Van Hire page to aid user planning. Priority: Should.
Unavailable pre-owned items: Instead of showing “no options available,” allow users to join a waitlist for their preferred store. Priority: Should.
Product filters for resale estimations: Organise the product catalogue with sorting options and filters. Priority: Could.
Outcome
A few months after this case study, IKEA indeed redesigned their website. While the website ultimately took a different form, it reflects the core recommendations I provided, demonstrating my ability to detect problems and design solutions that anticipate real-world outcomes.